DCGAN (Deep Convolutional General Adversarial Networks) uses convolutional layers in its design.
Architectural Details for DCGAN
- Comprised convolutional network without max-pooling. Instead, it uses convolutional stride and transpose convolution for downsampling and upsampling respectively. To find out how pooling and convolutional stride differs please go through this.
- Removed all fully connected layers
- Used batch normalization to bring stability in learning. It is done by normalizing the input to have zero mean and a variance of one. Batchnormalization was added to all the layers except generator output layer and discriminator input layer
- ReLU activation is used in the generator except for the output layer which uses tanh activation function
- LeakyReLU activation is used at all layers in the discriminator
Training Generator in DCGAN
[latexpage]
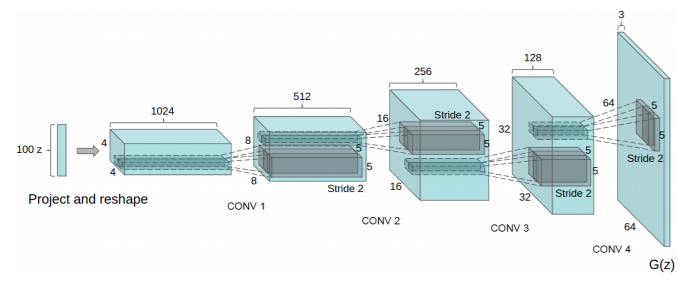
Generator takes a uniform noise distribution \(z\) as input. This input is reshaped with the help of fully connected layer into three dimensional layer with small base (width * height) and depth. Then, using transposed convolution, the output from previous layer is upsampled. Each transoposed convolution layer is followed by batch normalization to normalize the input. This helps in stabilizing the training of our GAN.
Details of Adversarial Training
DCGAN was trained on three datasets: Large-scale Scene Understanding (LSUN), ImageNet-1k and Faces dataset.
- Training images were scaled to the range of tanh activation function [-1, 1] and no further pre-processing was performed
- All models were trained with mini-batch size of 128
- Weights were initialized from normal normal distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation of 0.2
- Incase of LeakyReLU, the value of alpha was set to 0.2
- Adam optimizer was used for updating weights. Learning rate was set to 0.001 and momentum term was reduced to 0.5 from 0.9
Dataset Details
- DCGAN model was trained on LSUN bedroom dataset comprising over 3 million training images.
- No data augmentation was used
- De-duplication process was performed to decrease the likelihood of generator memorizing input examples. For this, autoencoder was trained to find and delete similar points from the training dataset. De-duplication process helped in removing 275k images.

Generated bedrooms after five epochs of training source

Generated bedrooms after five epochs of training source